Adapting participatory epidemiology to estimate the incidence of human diseases in Moroto District, Karamoja, Uganda
USAID

Adapting participatory epidemiology to estimate the incidence of human diseases in Moroto District, Karamoja, Uganda
This study explored the use of participatory epidemiology (PE) to estimate the annual incidences of human diseases in Karamoja, Uganda, with emphasis on diseases associated with water. Adapted PE methods were used successfully to estimate disease incidences in young children and adults, and revealed a rich knowledge on the clinical signs and causes of diseases. The report concludes that PE could be useful for overcoming some of the spatial limitations of the health surveillance system in Karamoja, and the temporal limitations of bi-annual food security and nutrition assessments.

Privatization of Land and its Impacts on Agro-Pastoral Livelihoods in Karamoja, Uganda: Case studies of Moroto and Nakapiripirit Districts
This report presents the findings of a review of land issues in Karamoja, with a particular focus on trends in privatization of communal lands and its impacts on agro-pastoral livelihoods.

Localized Approaches to Measuring Localization
In November 2021 United States Agency for International Development (USAID) announced a new global localization agenda that aims to shift more funding and decision-making to local organizations and groups. Under this agenda, USAID positioned local leadership over development and humanitarian assistance as important for aid effectiveness, equity, and sustainability.

Guidelines for Participatory Water Management and Development in Karamoja
Water resources support key sectors of the economy namely: hydropower generation, agriculture, fisheries, domestic water supply, industry and navigation among others. However, the efficiency and sustainability of water utilization has recently been a concern in Uganda mainly due to inadequate sectoral collaboration in planning and implementation, increasing frequency of floods and droughts, environmental degradation and pollution of water resources.

Localized Water and Rangeland Management in Karamoja: Lessons from a participatory review
Water and rangeland resources are the basis for livestock production in pastoralist areas of Africa and therefore have major impacts on pastoral livelihoods. Households with insufficient access to water or productive rangeland experience suboptimal herd growth and production, with associated negative impacts on the income and nutritious foods that livestock provide. In common with other African pastoralist and agropastoralist areas,

Early Warning and Disaster Response in Karamoja: The need to integrate local knowledge and formal systems
A genuine localized approach to early warning should shift the approach to more of a partnership and coacceptance of the strengths and weaknesses of indigenous and conventional systems.

KARAMOJA RESILIENCE SUPPORT UNIT: Turning Evidence Into Action
To gauge understanding of how KRSU’s work benefits and is utilized in Karamoja, a rapid review was conducted in November and December 2023. The review involved face-to-face interviews with a number of the organization’s partners – including non-governmental organizations (NGOs), universities, academics, and donors.

Analysis of Educational Approaches in Karamoja
This analysis is motivated by the concerns of international donors and other stakeholders regarding the persistent challenges in advancing educational outcomes for the majority of the population in the Karamoja sub-region of Uganda. Substantial improvements in enrolment and retention rates in Karamoja have occurred over the past eight years, but these remain significantly behind the national average, and drop-out rates after primary school are extremely high, especially for female students.i This analysis uses existing primary and secondary data to investigate various approaches for education in the sub-region.

WATER AND RANGELAND IN KARAMOJA
Water and rangeland resources are the basis for livestock production in pastoralist areas of Africa and therefore have major impacts on pastoral livelihoods. Households with insufficient access to water or productive rangeland experience suboptimal herd growth and production, with associated negative impacts on the income and nutritious foods that livestock provide.

INDIGENOUS EARLY WARNING IN KARAMOJA, UGANDA
An effective early warning system (EWS) is a prerequisite for timely response to avert and mitigate the impacts of disasters that affect pastoralist and agro-pastoralist communities. Whereas there exist various forms of EWS in Uganda, the main concerns have been whether the early warning information is timely, accurate, accessible, and elicits early action. These questions point at inefficiencies in the conventional EWS in the country and the importance of the indigenous early warning system (IEWS) used by rural communities. These indigenous systems are especially important where conventional early warning information is inaccessible or coarse and therefore not suitable for guiding location-specific decisions.

The 2022 Humanitarian Crisis in Karamoja, Uganda: A real-time review
This real-time review aims to document the events that led to Karamoja’s hunger crisis in 2022, the reporting of the worsening situation by early warning systems, and the responses of the Government of Uganda and the international aid community. The review took place from the September 27–October 21, 2022.

The 2022 Humanitarian Crisis in Karamoja: Findings from a real-time review
In July 2022 the Ugandan media reported that 900 people had died of hunger or hunger-related diseases in the Karamoja sub-region since February 2022, and that 8 out of 10 households had limited or no food.i

The Return of Conflict in Karamoja, Uganda: Community Perspectives
After nearly 10 years of relative peace, conflict and insecurity returned to the Karamoja sub-region of northeastern Uganda starting in 2019. This assessment investigates this resumption of conflict and insecurity from the perspective of the communities most involved and affected.

Conflict in Karamoja: A Synthesis of Historical and Current Perspectives, 1920-2022
This knowledge synthesis focuses on violent conflict in the Karamoja sub-region of northeastern Uganda. While violence and conflict both can and do take many forms, this synthesis takes as its focus the phenomenon of cattle raiding and associated violence. This knowledge synthesis briefly describes the concept and role of cattle raiding within pastoral societies in East Africa and the Karamoja Cluster and then examines different historical periods and experiences of violent conflict associated with cattle raiding within the Karamoja sub-region.

Educating Girls in Karamoja, Uganda: Barriers, Benefits, and Terms of Inclusion in the Perspectives of Girls, their Communities, and their Teachers
This scoping report investigates barriers, benefits, and “terms of inclusion” for girls’ education in the Karamoja sub-region of Uganda. Karamoja has some of the lowest education indicators in the country, with females generally faring much worse than males. The report examines the experiences and perceptions of girls, male and female community members, and teachers about girls’ education in the region, drawing on an assessment that took place from June to August 2022 in 10 sites in four districts: Amudat, Kaabong, Moroto, and Napak.

Education in East Africa’s Pastoralist Areas: Why are girls still not going to school?
This briefing paper presents learnings from global, and specifically East African, experience to support concerned stakeholders in thinking transformatively about education inclusion in Karamoja. While Karamoja is also home to agriculturalists, this paper focuses specifically on education among those pursuing livelihoods as pastoralists and agro-pastoralists, and particularly on the education of girls in those communities.

Karamoja Donor Mapping Report
This report summarizes planned humanitarian and development activities of major donors in the Karamoja sub-region

Food Security, Nutrition, and Conflict Assessment in Karamoja, Uganda
In mid-2020, the Karamoja Resilience Support Unit (KRSU) conducted a rapid assessment that described the impact of COVID-19 containment measures on rural livelihoods in Karamoja (Arasio et al. 20201). The assessment also forecast how disease restrictions would affect livelihoods over the following six to eight months (into early 2021). The initial assessment examined household wellbeing during COVID-19 relative to a normal (good) and bad (drought) year in Karamoja’s three main livelihood zones, represented by Amudat District (predominantly pastoralist but with some emerging crop production), Moroto District (predominantly agropastoralist), and Abim District (with high dependence on crop production, but also using livestock).

Tackling malnutrition: understanding local needs and factors behind seasonal hunger
Child malnutrition and stunting have posed challenges to populations in East Africa and the Horn of Africa for several decades. However, rates have not only continued to increase during this time, but now have a broader impact: for many years, it was primarily youngsters in agrarian communities that bore the brunt of the impact. Today, the effects are being experienced by both adults and children in pastoralist communities, and are exacerbated by ongoing population growth.

Livestock in Karamoja: improving markets and veterinary services
As Karamoja is a predominantly a pastoralist region, market trading of livestock is key to the region’s economy. However, a number of factors – ranging from policies and seasonality to price trends and market types – prevent livestock value chain actors from maximising their income and achieving livelihood security.

Improving practice: enhancing pastoralism policy
Although extensive research has been conducted into pastoralism, the sector – from its actors and systems to economic and environmental impacts – remains largely misunderstood. This is exacerbated by the fact that those living and working in pastoral communities often have trouble effectively expressing the processes they engage in and the benefits of pastoralism.

Fighting alcoholism in Karamoja
Following disarmament in Karamoja, north east Uganda, which began in 2010 and continues to date, the consumption, production and sale of alcohol experienced a dramatic increase. Consequently, health, household wealth and relationships have been significantly affected as a result of the negative effects on communities and individuals.

Drought Risk Management in Karamoja: Challenges and Opportunities
This Briefing Paper presents the main findings from the review report. The review considered the roles of the National Emergency Coordination Center (NECOC) and District Disaster Management Committees (DDMCs) in collecting and analyzing early warning information, and in timely response to drought.

Drought Risk Management in Karamoja: A Review of Functionality and Capacity
In the history of Karamoja, drought has been one of the most important types of disaster, with major impacts on livelihoods. For livestock-owning households, drought can push both wealthy and poorer households into destitution, and the recovery of herds, their main form of financial capital, takes many years. Drought also has serious impacts on crop production and can decimate harvests. In the case of livestock interventions, there have been notable developments in effective drought response in many countries in the wider East Africa region, including novel partnerships between government, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and private sector to provide early and more cost-effective programming.

Livestock in Karamoja, Uganda- The Economic Value of Agropastoral and Pastoral Systems
Across the East Africa region livestock are an important asset for rural households, and livestock products contribute to human nutrition, and to local, national and regional economies. However, in some countries there has been a longstanding issue of under-investment in the livestock sector, and this problem has been associated with official underestimates of livestock’s contribution to national economies.

RAPID ASSESSMENT OF COVID-19 IMPACTS IN KARAMOJA, UGANDA
This technical report describes the impacts of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) restrictions in the Karamoja sub-region of Uganda, based on field assessments in Amudat, Moroto and Abim Districts. The COVID-19 prevention guidelines that prompted total lockdown measures included market closure and travel restrictions which in turn affected the essential economic activities of many households, especially the poor.

The Productivity and Economic Value of Livestock in Karamoja Sub-Region, Uganda
Across the East Africa region livestock are an important asset for rural households, and livestock products contribute to human nutrition, and to local, national and regional economies. However, in some countries there has been a longstanding issue of under-investment in the livestock sector, and this problem has been associated with official underestimates of livestock’s contribution to national economies.

THE PRODUCTIVITY AND ECONOMIC VALUE OF LIVESTOCK IN KARAMOJA SUB-REGION, UGANDA
This report calculates the direct use value of livestock in Karamoja Sub-region, Uganda. The concept of direct use value pulls together under one heading all the various economic benefits derived from livestock.

Certification Test Training For Adaptation and Roll-out of Pastoralism and Policy Course
The Karamoja Resilience Support Unit (KRSU), in partnership with the International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED), commissioned the adaptation and roll-out of the East African Pastoralism and Policy Course (PPC) and has completed the final training of trainers (ToT) course.

Fifth Training of Trainers Workshop for Roll-out of Pastoralism and Policy Course
The Karamoja Resilience Support Unit (KRSU), in partnership with the International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED), commissioned the adaptation and roll-out of the East African Pastoralism and Policy Course (PPC) and has completed the final training of trainer’s (ToT) course.

Fourth Training of Trainers Workshop for Roll-out of Pastoralism and Policy Course
The Karamoja Resilience Support Unit (KRSU), in partnership with the International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED), commissioned the adaptation and roll-out of the East African Pastoralism and Policy Course (PPC) and has completed the final training of trainer’s (ToT) course.

Hidden Peaks: Women’s Knowledge on the Seasonality and Root Causes of Child Malnutrition in Karamoja, Uganda and Their Programming Preferences
This report from the KRSU uses participatory epidemiology to understand women’s knowledge on the seasonality and causes of child malnutrition in Karamoja. The report provides important new information on the timing of peaks in child malnutrition, women’s views on the main causes of malnutrition and the relative importance of these causes, and women’s preferences for programs to reduce malnutrition

Third Training of Trainers Workshop for Roll-out of Pastoralism and Policy Course
The Karamoja Resilience Support Unit (KRSU), in partnership with the International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED), commissioned the adaptation and roll-out of the East African Pastoralism and Policy Course (PPC) and has completed the final training of trainer’s (ToT) course.

LIVESTOCK AND POVERTY IN KARAMOJA AN ANALYSIS OF LIVESTOCK OWNERSHIP, THRESHOLDS, AND POLICY IMPLICATIONS
In pastoralist and agro-pastoralist households in East Africa, livestock not cash are usually the main financial asset. Animals are sold to buy grain and to meet other domestic needs, and animals also provide food, especially milk, for direct human consumption.

Livestock and Poverty in Karamoja – An Analysis of Livestock Ownership, Thresholds, and Policy Implications
This report analyses poverty in Karamoja from the perspective of livestock ownership, and uses a livestock threshold to categorize households as poor and non-poor. High levels of livestock poverty are then discussed in relation to programming and policy options

THE SILENT GUN: CHANGES IN ALCOHOL PRODUCTION, SALE, AND CONSUMPTION IN POST-DISARMAMENT KARAMOJA, UGANDA
Research and observations over the past decade have pointed to the high prevalence of alcohol use in Karamoja. Brews made locally of sorghum and maize have sociocultural, nutritional, and economic significance.

Agriculture in Karamoja-The need for integrated livestock-crop development
This Policy Brief explores the role of agriculture in Karamoja’s development, and in particular, the need to support balanced and integrated livestock-crop strategies.

Second Training of Trainers Workshop for Roll-out of Pastoralism and Policy Course
The Karamoja Resilience Support Unit (KRSU), in partnership with the International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED), commissioned the adaptation and roll-out of the East African Pastoralism and Policy Course (PPC) and has completed the final training of trainer’s (ToT) course.
Livestock Trade Dynamics in Karamoja-Trends in market activity and policy issues
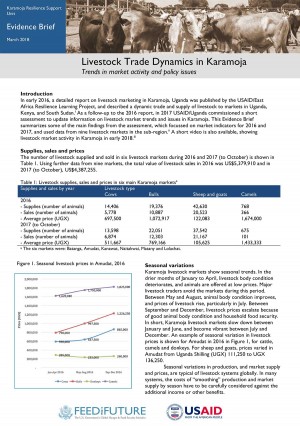
In early 2016, a detailed report on livestock marketing in Karamoja, Uganda was published by the USAID/East Africa Resilience Learning Project, and described a dynamic trade and supply of livestock to markets in Uganda, Kenya, and South Sudan. As a follow-up to the 2016 report, in 2017 USAID/Uganda commissioned a short assessment to update information on livestock market trends and issues in Karamoja.

AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN KARAMOJA, UGANDA: RECENT TRENDS IN LIVESTOCK AND CROP SYSTEMS, AND RESILIENCE IMPACTS
This report is a review of agricultural development trends in the Karamoja sub-region of northeast Uganda. The review covered both crop farming and transhumance livestock management and examined agriculture at the levels of both policy and programming.
Livestock Trade Dynamics in Karamoja
In early 2016, a detailed report on livestock marketing in Karamoja, Uganda was published by the USAID/East Africa Resilience Learning Project, and described a dynamic trade and supply of livestock to markets in Uganda, Kenya, and South Sudan.

Training of Trainers Pastoralism and Pastoral Policy Course (One)
The Karamoja Resilience Support Unit (KRSU), in partnership with the International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED), commissioned the adaptation and roll-out of the East African Pastoralism and Policy Course (PPC) and has completed the final training of trainer’s (ToT) course.

PASTORALIST AND LIVESTOCK DEVELOPMENT IN KARAMOJA, UGANDA
This review examines regional policies and programming initiatives in East Africa and the Horn of Africa related to pastoral areas development, and their relevance to the Karamoja Region of Uganda.

LOOKING FOR WORK: WAGE LABOR, EMPLOYMENT, AND MIGRATION IN KARAMOJA, UGANDA
The main purpose of this assessment is to document and analyze trends in labor and employment in the non-pastoral labor sectors within and outside Karamoja, and to investigate how individual- and macrolevel factors influence participation in the labor market.

Financial Services in Karamoja A Rapid Review
The review is an initial exploratory and rapid assessment of financial services in the region and was conducted over a short time frame. The aim to flag issues for more detailed analysis and follow up, rather than being a comprehensive study on financial services.

VETERINARY SERVICES IN KARAMOJA, UGANDA: A REVIEW
This aim of this report is to document the experiences of veterinary service delivery in Karamoja and draw lessons to guide a strategy for future service provision, aligned to Uganda’s animal health policies and legislation.

Veterinary Services in Karamoja, Uganda: A Review
The KRSU has recently completed a comprehensive review of veterinary services in Karamoja. The review covers all aspects of public and private sector service delivery, and reports the persistent high impacts of livestock diseases on livelihoods. The review recommendations include the need for stronger coordination of veterinary projects and programs, better support to community-based systems, and improving linkages between private veterinary pharmacies and community-basd animal health workers.

Karamoja Donors Mapping Report
A mapping of 2017 funds to Karamoja from 10 major bilateral and multilateral donors. Additional Information This donor mapping exercise has been compiled by the USAID supported Karamoja Resilience Unit (KRSU), on behalf of the KDPG. This is the second year that the KDPG has produced this mapping exercise. This year it is estimated that these 10 donors will provide €89 million (approx. 380 billion Ugx) during 2017. The analysis provided in this report (see Section 2) demonstrates that this funding is provided across all sectors with a particular focus on the basic service delivery (KIDP strategic objective 1) and food security (KIDP strategic objective 6).

Livestock for Livelihoods- Priorities for livestock development in Karamoja, Uganda
Many areas of East Africa are responding to growing demands for livestock products, from both within the region and internationally. In Ethiopia and Kenya, pastoralist and agropastoralist producers supply most of the animals and milk to domestic markets, and live animals and chilled meat for export. This supply from the region’s drylands is supported by a changing policy environment at regional and national levels, with increasing recognition of the economic contributions of extensive, mobile livestock production systems, and the value of these systems in areas with highly variable rainfall.

A Better Balance: Revitalized Pastoral Livelihoods in Karamoja, Uganda
Livelihoods in Karamoja continue to change as security improves; this includes a revitalization of pastoral production for some households. This report details the findings from research undertaken in February and March 2016 in four districts of Karamoja aimed at better understanding the current patterns of pastoral and agro-pastoral production in the region.

Livestock in Karamoja: A review of recent literature
The review synthesizes the main issues impacting livestock production in the region and identifies critical factors affecting livestock production. This review is drawn largely from the literature produced during the last five years on Karamoja generally, and more specifically on the livestock sector in Karamoja. Additional information was obtained through interviews in Kampala and Moroto with Government and NGO staff in April and May 2016.

Livelihood diversification trends, risks, and programming implications
This study explored recent trends in diversification by East African pastoralists, the factors that drive their choices, and the potential short and longer-term consequences of their decisions. It considered the risks and costs of diversified and alternative livelihoods, as well as the benefits. The report presents findings from three case studies from Karamoja in northeastern Uganda, the Borana region of southern Ethiopia, and the Garissa District of northeastern Kenya. It includes policy recommendations regarding land tenure, local value addition around livestock production, and investments in sustainable natural products, local infrastructure, and urban/peri-urban planning. Further recommendations address nutritional issues, the promotion of regional trade, and growing demands for education, training, and business development skills.

Karamoja Livestock Market Assessment Report
This report presents an analysis of livestock marketing in the Karamoja region of north-east Uganda. This assesment reviews the current status of livestock marketing and trade in Karamoja, including cross-border trade with Kenya and South Sudan. The assessment explains the economic logic of herd growth in Karamoja as a means to build household financial capital, and questions the notion of Karamojong herders as unresponsive to price and opportunity. The assessment reports a practice of 'trading up' in which bulls are fattened and exchanged for heifers, as well as a dynamic livestock market activity in Karamoja. Key constraints to livestock production are highlighted - weak veterinary services and problems with livestock water supply.

“We Now Have Relative Peace”; Changing Conflict Dynamics in Northern Karamoja, Uganda
This report reflects research from early 2015 conducted by the Feinstein International Center at the Friedman School of Tufts University and Mercy Corps in northern Karamoja, Uganda. The research examined changing conflict dynamics and related conflict mitigation and peacebuilding initiatives. The objective of the study was to provide a nuanced understanding of the current threats to security at the household, community, district and regional levels, and to examine how these dynamics have changed in recent years. The study examined conflict mitigation initiatives, including access to and efficacy of these systems.

“We Now Have Relative Peace” ; Changing Conflict Dynamics in Northern Karamoja, Uganda
The objective of the study was to provide a nuanced understanding of the current threats to security at the household, community, district and regional levels, and to examine how these dynamics have changed in recent years.

Protecting Milk Supply to Pastoralist Children: Good Practice from the Milk Matters Project in Ethiopia
This technical brief provides an overview of Milk Matters, how it was designed, and the results achieved. The brief summarizes the key lessons from the project and discusses the need for further testing of the approach in other countries. The brief also asks whether Milk Matters might be used to reduce chronic malnutrition or stunting. In mid-2008 workers from Save the Children and Tufts University in Ethiopia came together to try to better understand and address the longstanding problem of acute malnutrition in pastoralist children.With funding from the US Office for Foreign Disaster Assistance, the Milk Matters project was started and worked with Somali pastoralists in Ethiopia to design and test new approaches for preventing wasting. Central to the approach was recognition of the seasonality of food access in pastoralist areas, and the high nutritional value of animal milk. It was also known that the long dry season was the critical period in terms of the risk of acute child malnutrition, due to declining access to milk at this time.

Community-based Animal Health Workers: Where Are We Now? Lessons from Ethiopia, Kenya, and South Sudan
A policy brief on evidence on community-based animal health workers in Ethiopia, Kenya, and South Sudan. At community-level, CAHWs are seen as valuable service providers and outperform other types of animal health care in most aspects of service provision. The main constraint is the supply of veterinary medicines in contexts of mixed policy support to veterinary privatization and limited government capacity to ensure the quality of imported or locally-manufactured medicines. In Kenya, these issues are compounded by a lack of policy or legislative support to CAHWs, combined with weak service provision by other providers in pastoralist areas

Community-Based Animal Health Workers in the Horn of Africa: An Evaluation for the Office of Foreign Disaster Assistance
Evaluation of USAID Office of Foreign Disaster Assistance (OFDA)-funded Community-Based Animal Health Worker (CAHW) programs in the Horn of Africa

Animal Health Sector Assessment Report (Abim, Kaabong, and Kotido)
The Animal Health sector assessment was conducted by the team of 3 members; Gratian, Juliet and Regina in Abim, Kotido, Kaabong and outside Karamoja in Lira, Soroti and Mbale to understand the systemic functionality; major players, development actors, support functions, loopholes and challenges, actor/agency relations, drug supply chain as well as the formal and informal rules governing the sector.

Livelihood Dynamics in Northern Karamoja: A Participatory Baseline Study for the SUSTAIN Project
This report documents the findings of a livelihoods assessment carried out as part of the USAID funded Sustainable Transformation in Agriculture and Nutrition (SUSTAIN) project being implemented by Mercy Corps and partners in the Karamoja sub-region of Northeastern Uganda. The overall goal of the SUSTAIN project is to promote peace and food security through three complementary strategic objectives aimed at (1) strengthening livelihoods, (2) improving nutritional outcomes for children under two and (3) building local capacities for conflict mitigation.The project is being implemented in three districts of Northern Karamoja, Abim, Kaabong and Kotido. The objective of this particular study is to inform implementation and collect baseline impact indicators for the activities under objective # 1. Under this objective (livelihoods strengthening)the project aims to improve productivity, market access, marketing behaviors and the overall business environment.
